Mechanical Thrombectomy Procedure for Stroke in Chennai
What Is Mechanical Thrombectomy?
Mechanical thrombectomy is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove a blood clot from a blocked artery in the brain. It is an established treatment for ischemic stroke, a condition caused by reduced blood flow to brain tissue due to a clot.
Unlike intravenous thrombolysis (IV tPA), which is effective only within a limited time window, the mechanical thrombectomy procedure can be performed up to 24 hours after symptom onset in selected patients, based on advanced brain imaging and clinical assessment.
- Why it matters:Stroke causes rapid brain cell damage. Early restoration of blood flow through mechanical thrombectomy can reduce brain injury and improve neurological outcomes.
Who Is Eligible for Mechanical Thrombectomy Procedure?
A patient may be considered for the mechanical thrombectomy procedure if they:
- Have a large vessel ischemic stroke
- Reach a stroke-ready hospital within 6 to 24 hours of symptom onset
- Show salvageable brain tissue on CT or MRI Imaging
- Are evaluated by a neurologist or neurointervention specialist
Eligibility depends on imaging findings and clinical status, rather than time alone.
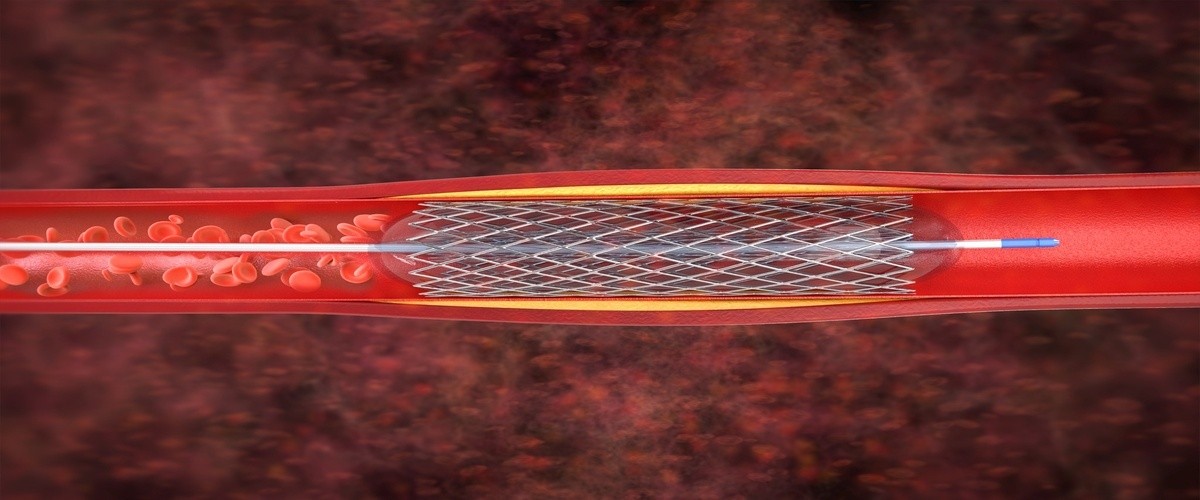
Mechanical Thrombectomy Procedure: Step by Step
- Vascular Access
A thin catheter is inserted through the artery in the groin or wrist and guided towards the brain. - Navigation to the Clot
Using real-time imaging, the catheter is carefully advanced to the site of the arterial blockage. - Clot Removal
Specialized devices such as stent retrievers or aspiration catheters are used to capture and remove the clot. - Restoration of Blood Flow
Angiography confirms the reopening of the blocked vessel and restoration of cerebral blood flow. - Post-Procedural Care
Patients are monitored in a critical care unit, followed by medical management and stroke rehabilitation as needed.
Benefits of Mechanical Thrombectomy
Clinical studies and real-world experience show that patients undergoing this procedure may experience:
- Faster neurological improvement
- Higher likelihood of functional independence at 90 days
- Reduced extent of brain damage
- Improved outcomes when combined with IV thrombolysis in eligible cases
Risks and Limitations
As with any medical procedure, there are some risks:
Potential Risks
- Intracranial bleeding
- Injury to blood vessels
- Fragmentation of migration of clots
Limitations
- Requires advanced neurointerventional facilities
- Not suitable if irreversible brain damage has occurred
- Needs close post-procedure monitoring and rehabilation support
Real-World Impact
“We treated a patient who presented with sudden speech loss and paralysis on one side. Following mechanical thrombectomy, neurological improvement was seen within hours, with early mobilization possible the next day.”
– Dr. Aravinth Kumar A, Senior Neurologist, MGM Healthcare Malar
Mechanical Thrombectomy in Chennai
Mechanical thrombectomy requires a coordinated stroke care system that includes rapid imaging, experienced specialists, and post-stroke rehabilitation.
MGM Healthcare Malar provides:
- Round-the-clock stroke evaluation
- Advanced CT and MRI Imaging
- Multidisciplinary rehabilitation support
Visit: MGM Neurosciences Department
Call: 099625 99933
Final Thoughts
The mechanical thrombectomy procedure has significantly changed the management of acute ischemic stroke. Early recognition of symptoms and prompt medical evaluation are essential for improving outcomes. Patients and families seeking timely stroke assessment may contact the care team to understand the next steps.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The mechanical thrombectomy procedure is a minimally invasive method used to remove a clot from a blocked brain artery in patients with ischemic stroke.
The procedure typically takes30 to 90 minutes, depending on the location of the clot and patient condition.
It is not open surgery. Mechanical thrombectomy is an endovascular procedure performed through blood vessels using catheters.
When performed at experienced stroke centres, the procedure is considered safe, though risks such as bleeding or vessel injury may occur.
Recovery varies by patient. Some show improvement within hours or days, while others require longer rehabilitation depending on stroke severity.
Contact Us
Appointments
Emergency
MGM - Malar Adyar
Old No. 52 New No. 111, 1 st Main Road, Gandhi Nagar, Adyar, Chennai – 600020
At MGM Malar - Adyar Hospital, our philosophy centers on alleviating the apprehension associated with illness. Recognizing that confronting health challenges entails both physical and emotional struggles, our devoted team is steadfast in delivering outstanding healthcare to enhance your overall wellness and alleviate the stress that accompanies medical conditions. Situated in the heart of the city with a 141-bed facility, we are dedicated to supporting you throughout your healthcare journey.